Sec. 23.443 - Gust loads.
(a) Vertical surfaces must be designed
to withstand, in unaccelerated flight at speed VC,
lateral gusts of the values prescribed for VC in
§23.333(c).
(b) In addition, for commuter category
airplanes, the airplane is assumed to encounter derived gusts normal to
the plane of symmetry while in unaccelerated flight at VB, VC,
VD, and VF. The derived gusts and airplane speeds
corresponding to these conditions, as determined by §§23.341 and 23.345,
must be investigated. The shape of the gust must be as specified in
§23.333(c)(2)(i).
(c) In the absence of a more rational
analysis, the gust load must be computed as follows:
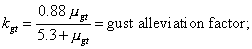
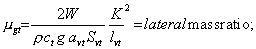
Ude=Derived gust velocity (f.p.s.);
ρ=Air density (slugs/cu.ft.);
W=the applicable weight of the airplane in the particular load case
(lbs.);
Svt=Area of vertical surface (ft. 2);
c
t=Mean geometric chord of vertical surface (ft.);
avt=Lift curve slope of vertical surface (per radian);
K=Radius of gyration in yaw (ft.);
lvt=Distance from airplane c.g. to lift center of vertical
surface (ft.);
g=Acceleration due to gravity (ft./sec. 2); and
V=Equivalent airspeed (knots).
[Amdt. 23-7, 34 FR 13090, Aug. 13, 1969, as amended by Amdt.
23-34, 52 FR 1830, Jan. 15, 1987; 52 FR 7262, Mar. 9, 1987; Amdt. 23-24,
52 FR 34745, Sept. 14, 1987; Amdt. 23-42, 56 FR 353, Jan. 3, 1991; Amdt.
23-48, 61 FR 5147, Feb. 9, 1996]