|
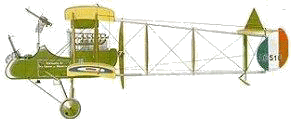
Initially used for reconnaissance, the Farman Experimental 2 two-seater
biplane ended the "Fokker Scourge" over the Somme. Like the single-seat
D.H.2, it was a "pusher" and items floating about in the nacelle
inevitably ended up being swept back into the propeller, sometimes with
disastrous results. Armed with two or three Lewis guns and a camera,
the observer sat far forward in the nacelle, directly in front of the
pilot. Vulnerable to attacks from rear, the F.E.2 was frequently shot
down. During the summer of 1916, the Germans captured one of the first
F.E.2d's when a British pilot inadvertently landed his new aircraft at
an enemy aerodrome. The introduction of more advanced aircraft made the
F.E.2 an ineffective fighter and by 1917 it was primarily used for
bombing missions.
RAF F.E.2d
Manufacturer: Royal Aircraft Factory
Type: Fighter/Bomber
First Introduced: 1915
Number Built: About 1,000
Engine: Inline rotary, Beardmore 160 hp
Wing Span: 47 ft 9 in 14.56 m
Length: 32 ft 3 in 9.83 m
Height: 12 ft 7½ in 3.84 m
Empty Weight: 935 kg
Gross Weight: 3,037 lb 1,378 kg
Max Speed: 91½ mph 150 km/h
Ceiling: 11,000 ft 3,300 m
Endurance: 2 hr 30 min
Crew: 2
Armament: 2 or 3 .303 Lewis machine guns |
