|

Clement Ader Avion 3
Eole


The French
experimenter Clement Ader investigated bird and bat flight and began to
construct glider models in 1872. His first full-size aircraft, a monoplane
called the Eole after the Greek god of the wind, had a bat-like
structure. An efficient alcohol-fired 10-to-12-horsepower (7.5-to-9-
kilowatt) steam engine, which was considerably lighter than the
12-to-16-horsepower (9-to-12- kilowatt) engine on the Wright Flyer, was
mounted on the fuselage. The engine drove a large 8.5- foot (2.6 meter)
tractor propeller. With Ader's weight, the Eole weighed about 727
pounds (330 kilograms) and had heavily cambered wings spanning more than
39.4 feet (12 meters).
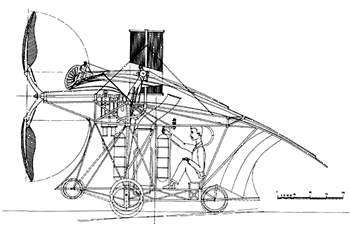
Clément Ader's Eole,
(Side Elevation Alt.)
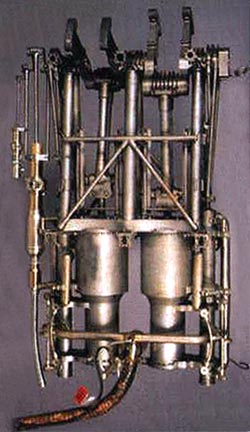
Clément Ader's Eole,
Motor
Ader tested
the Eole on October 9, 1890, over a 656.2-foot (200 meter) prepared
surface at the Chateau d'Armainvilliers in Brie, southwest of Paris.
Witnesses saw it hop about 165 feet (50 meters) as it rose a few inches
off the ground, becoming the first manned, steam-powered craft to rise
from level ground. However, the flight could not be sustained and did not
achieve control. Ader also lacked the piloting skills to deal with the
wind gusts and crosswinds that blew him off the track. Even so, he was
encouraged by his success and continued experimenting using similarly
configured machines.
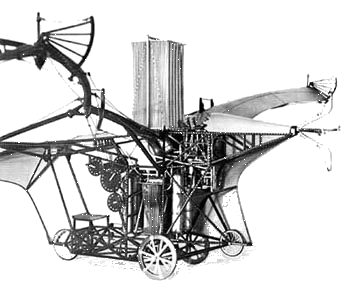
|
