|

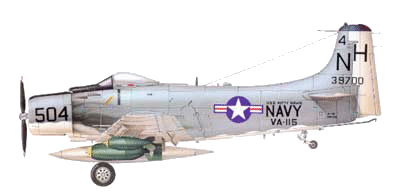
Douglas A-1 Skyraider

The Skyraider was the last great single-seater
combat plane with a piston engine. Designed during the last years of World
War Two as a dive-bomber, and torpedo-carrier, it proved itself more
versatile and efficient than even its makers had imagined. The Douglas AD
(as it was designated) proved its worth during the jet era, first in
Korea, where it covered itself with glory, and then in Vietnam, so much so
that in 1966 (nine years after the closure of the production lines which,
from 1947 to 1957, had turned out 3,180 aircraft in seven basic versions)
serious consideration was given to resuming production. The first
prototype flew on March 18, 1945 and operational service began in December
1946, with the AD-1 (277 machines). There then followed 178 AD-2s, 193
AD-3s and 1,051 AD-4s. All these versions had four main roles: daytime and
all-weather attack, radar patrol, and electronic countermeasures. In 1951
the variant two-seater AD-5 appeared, with a bigger cabin, and a year
later production resumed of the single-seater AD-6 (713 machines). The
last series was the AD-7 (72 planes) in 1955.
The Skyraider played a key role in the
Vietnamese conflict, especially in the early years. Powerfully armed,
slower than a jet aircraft, it came the closest to having the same
characteristics as the anti-guerrilla COIN, which at that time was
desperately in demand. The A-1Hs were originally designated the
single-seat AD-6s, and the A-1Es the two-seat AD-5s, last generation of
the Skyraiders. At the time of the Gulf of Tonkin crisis, in August 1964,
all aircraft carriers of the 77th Task Force had attack squadrons of
Douglas A-1Hs, which were among the first sent into action against targets
in North Vietnam. Two of them even achieved the incredible feat of
shooting down two jet-engined MiG-17s. The US Navy Skyraiders remained at
the front until April 1968, earning the nickname of 'Workhorse of the
Fleet' and losing 48 machines, mainly from anti-aircraft fire. A number of
aircraft of this type (25) surplus to Navy requirements, were also
assigned to the VNAF, the first six in September 1960, the other ones in
March 1961, as replacements for the obsolete North American T-28. But even
the USAF sent a few twin-seater A-1Es to the front in summer 1963, when
the 1st Air Command Squadron was formed. Useful for low-level attacks, and
ideal as escorts for rescue missions, during the early years of the war
they did everything and flew everywhere, being given the familiar name of
'Spad' from the famous World War One fighter. Skyraider, the last piston-engined
fighter aircraft of the US Navy, carried out some 100,000 missions in the
skies of Vietnam prior to its final disappearance .


Technical Specification
Aircraft:
Douglas A-1H
Year:1952
Type: attack
Manufacturer: Douglas Aircraft Co.
Engine: Wright R-3350-26WA, radial, 18 cyl., air cooled
Power: 2738hp
Wingspan: 50ft (15.24m)
Length: 39ft 2in (11.83m)
Height: 15ft 8in (4.77m)
Wing area: 400.33sq ft (37.19mē)
Max take-off weight: 25,000 lb (11,340 kg)
Empty weight: 11,968 lb (5,429 kg)
Max speed: 322mph at 18,000ft (518km/h at 5,846m)
Service ceiling: 28,510ft (8,690m)
Range: 1,142mi (1,840km)
Crew: 1
Load-armament: 4x20mm cannon; 7,960 lb (3,630 kg)
|
