To meet an Imperial
Japanese Army specification of December 1937 for a ground-attack
aircraft, which it was suggested could be a development of the Ki-30
light bomber. Great emphasis was placed on manoeuvrability, protection
for the crew and the capability of operating from emergency airfields
located near the combat area. Specifications called for a maximum speed
of no less than 260 mph (420 km/h) at 6,578 ft (2000 m), take-off
weight was to be 5,960 lbs (2700 kg) and it was to have a bombload of
at least 440 lbs (200 kg) and defensive armament consisting of three
machine guns, one which was on a moveable mounting. Mitsubishi produced
two prototypes under the designation Mitsubishi Ki-51 in the summer of
1939. Of similar external appearance to the Ki-30, the new design was
generally of smaller dimensions, had a revised and simplified cockpit
that put the two-man crew more closely together and, because the bomb
bay was not required, the monoplane wing was moved from a mid to
low-wing configuration. Powerplant chosen was the Mitsubishi 940 hp
(701 kW) Ha-26-II radial engine.
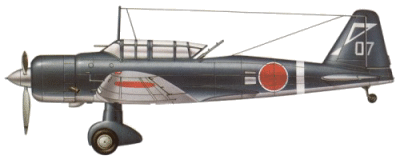
Tested during the
summer of 1939, the two prototypes were followed by 11 service trials
aircraft, these being completed before the end of the year. They
differed from the prototypes by incorporating a number of
modifications, but most important were the introduction of fixed
leading-edge slots to improve slow-speed handling and armour plate
beneath the engine and crew positions. Ordered into production in this
form as the Army Type 99 Assault Plane, the Ki-51 began a production
run that totalled 2,385 aircraft, built by Mitsubishi (1,472) and by
the First Army Air Arsenal at Tachikawa (913), before production ended
in July 1945. In addition to the standard production aircraft, there
were attempts to develop dedicated reconnaissance versions, initially
by the conversion of one Ki-51 service trials aircraft which had the
rear cockpit redesigned to accommodate reconnaissance cameras. Test and
evaluation of this aircraft, redesignated Ki-51a, brought a realisation
that the standard Ki-51 could be modified to have provisions for the
installation of reconnaissance cameras, and this change was made on the
production line. Subsequently, three Ki-71 tactical reconnaissance
prototypes were developed from the Ki-51, introducing the 1,500 hp
(1119 kW) Mitsubishi Ha-112-II engine, retractable landing gear, two
wing mounted 20 mm cannon and other refinements, but no production
examples were built.
Allocated the Allied
codename 'Sonia', the Ki-51 was used initially in operations against
China, and was deployed against the Allies until the end of the Pacific
war .In more intensely contested areas the fairly slow Ki-51s were easy
prey for Allied fighters, but in secondary theatres, where an ability
to operate from rough and short fields was valuable, these aircraft
gave essential close support in countless operations. In the closing
stages of the war they were used in Kamikaze attacks.
Variants
Mitsubishi Ki-51a - A
single Ki-51 conversion resulted in the Ki-51a tactical reconnaissance
prototype. Never put into production.
Mitsubishi Ki-71 -
Mitsubishi designed and Tachikawa arsenal built three prototypes of a
dedicated tactical reconnaissance aircraft powered by the 1,500 hp
(1119 kW) Ha-112-II engine and equipped with retractable landing gear.
Never put into production.
(Army Type 99 Assault
Plane - Mitsubishi Ki-51)
Allied Codename:
Sonia
Type: Two Seat
Ground Attack & Reconnaissance
Design:
Mitsubishi Jukogyo KK Design Team (Kawano, Ohki and Mizuno, who had
designed the Ki-30)
Manufacturer:
Mitsubishi Jukogyo KK (1,472) & Tachikawa Dai-Ichi Rikugun Kokusho (1st
Army Air Arsenal - 913)
Powerplant: One
1,500 hp (1119 kW) Mitsubishi Ha-26-II radial engine.
Performance:
Maximum speed 264 mph (425 km/h) at 9,845 ft (3000 m); service ceiling
27,130 ft (8270 m).
Range: 659 miles (1060 km) on internal fuel.
Weight: Empty
4,129 lbs (1875 kg) with a maximum take-off weight of 6,437 lbs (2920
kg).
Dimensions: Span
39 ft 8 1/4 in (12.10 m); length 30 ft 2 1/4 in (9.20 m); height 8 ft
11 1/2 in (2.73 m); wing area 258.56 sq ft
(24.02 sq m).
Armament: Two
fixed forward firing 7.7 mm (0.303 in) Type 97 machine guns, one 7.7 mm
(0.303 in) Type 92 machine gun on a trainable mount in rear cockpit
plus a bombload of up to 441 lbs (200 kg). On late model aircraft the
two fixed 7.7 mm guns were replaced by 12.7 mm (0.50 in) machine guns.
Variants: Ki-51a (single prototype), Ki-71.
Avionics: None.
History: First
flight summer 1939; first flight (Ki-71) 1941; production ended with
Japan's surrender.
Operators: Japan
(Imperial Japanese Army).
