|

The most important Italian bomber of World War II, this tough
three-engined aircraft established a reputation that contrasted with
most Italian weapons of the day, and it was flown with courage and
skill.
It
was the most important Italian bomber of World War II, this tough
three-engined aircraft established a reputation that contrasted with
most Italian weapons of the day, and it was flown with courage and
skill. SM.79s served widely in the normal bombing role; but it is as a
land-based torpedo bomber that the type deserves its place in military
aviation history, being regarded by many as one of the finest torpedo
bombers of the war.
The prototype appeared in late 1934 and subsequently had a varied
career, setting records and winning races with various engines and
painted in civil or military markings. The basic design continued the
company's tradition of mixed construction with steel tubes light alloy
wood and fabric (this being the only way to produce in quantity with
available skills and tools); but compared with other designs it had a
much more highly loaded wing which demanded long airstrips,
The prototype SM.79 had flown on 2 September 1935, powered by three 750
hp AlfaRomeo 125 RC.34 engines, and so following the Regia
Aeronautica's preferred tri-motor formula. About 1,300 production
models were built over a nine year period. They had internal provision
for 2,750 lb (1,250 kg) of bombs, supplemented by under fuselage racks
for a pair of heavy bombs, or two torpedoes in the case of the SM.79-II
and SM.79-III.
The SM.79 had a distinctive 'hump' on the upper forward fuselage, which
housed both the fixed forward-firing heavy machine-gun and the dorsal
gunner's position. Its appearance earned the aircraft the nickname 'Gobbo
Maleditto' ('Damned Hunchback'). In spite of its cumbersome appearance
and outdated steel tube/wood/fabric construction, the S.M.79 was a
rugged, reliable multi-role medium bomber which did quite a bit of
damage in the face of heavy opposition.
Developed from a civil airliner, the first Sparvieros entered service
with the Regia Aeronautica in late 1936, just in time to fly combat
over Spain with the Aviacion Legionaria, the Italian contingent
fighting in support of the Nationalists. The SM.79-I established an
excellent reputation in combat with the Aviacion Legionaria in Spain in
1936-1939. Its performance drew favourable comments from both sides,
leading to a succession of export orders. The SM.79-I served with the
Italian Aviazione Legionaria in support of Franco in the Spanish Civil
War.
In October 1939 the Regia Aeronautica began to receive the 79-II with
745.2 kW (1,000 hp) Piaggio P.XI RC.40 engines (one batch had the Fiat
A.80 of similar power) and this was the dominant version in action
subsequently. About 1,200 served with the Regia Aeronautica including a
handful of the III sub-type with forward-firing 20 mm cannon and no
ventral gondola.
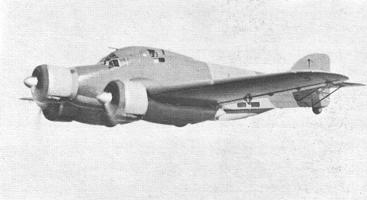
The SM.79 had a distinctive 'hump' on the upper forward fuselage. Its
appearance earned the aircraft the nickname 'Gobbo Maleditto' ('Damned
Hunchback').
When Italy joined the war in 1940 its air force had nearly 1,000
bombers, of which well over half were Savoia-Marchetti S.M.79 Sparviero
(Hawk) medium bombers. These trimotors, were thought by many to be
among the best land-based torpedo bombers of the war. They could carry
1,250 kg (2,750 lb) of bombs internally or two torpedoes. Also active
as a medium bomber around the Mediterranean and on anti-ship duties was
the Cant Z.1007bis Alcione (Kingfisher) ,production of which
began in 1939. It also was a trimotor, powered by 1,000 hp Piaggio
radials, and it carried four machine guns for self-defence as well
as up to 2,000 kg (4,410 lb) of bombs or two torpedoes.

In
the summer of 1942, Allied efforts to relieve beleaguered Malta
culminated in 'Operation Pedestal', when 14 merchantmen with heavy
Royal Navy escort left Gibraltar on August 10. Among the enemy aircraft
sent against them were 74 Sparvieri (Sparrow Hawks), a number of
which had already scored hits on the battleship HMS Malaya and the
carrier HMS Argus. 'Pedestal' eventually got through to Malta, but at
the cost of one carrier, two cruisers, a destroyer and nine merchant
ships, many of them having been hit by torpedoes from the S.M.79s.
The more powerful SM.79-II served in North Africa, the Balkans, and
Mediterranean during the Second World War, while other units called
Aerosiluranti (aerial torpedoes) pioneered use of these large fast
bombers in the anti-shipping role. When the Italians surrendered on
September 8,1943, it did not end the combat record of the SM.79, and a
new version, the SM.79-III torpedo-bomber, was placed in production by
the RSI, the fascist government in northern Italy.
An effective torpedo bomber as well, the S.M.79 served in the air
forces of Brazil, Iraq, Yugoslavia, Romania and Spain, some right up to
the end of the war. The Romanians flew them on the Russian front from
1941 to 1944, an unprecedented record for an aircraft designed in the
early 1930s. Though known as a tri-motor, several versions were built
as twin-engined aircraft using a number of different powerplants,
including Junkers Jumo 211 D 1,220 hp inlines. Regardless of the
version, its handling pleased most pilots and its ability to come home
with extensive damage endeared it even more. Used throughout North
Africa and the Mediterranean until the Italian surrender in September
1943, the Sparviero remained flying with both the Italian
cobelligerent forces fighting alongside the Allies and the surviving
pro-Nazi units.
About 100 were exported to Brazil Iraq and Romania - all of the
twin-engined S.M. 79B variety. Romania built the 79JR under license
with two 894 kW (1,200 hp) Junkers Jumo 211Da liquid-cooled
engines. These were used in numbers on the Eastern Front; initially as
bombers with visual aiming position in the nose and subsequently mainly
as utility transports.
Post-war surviving SM.79s were converted into various versions of
utility transports during the last phases of the war and survived in
that role until 1952.

An effective torpedo bomber as well, the S.M.79 served in the air
forces of Brazil, Iraq, Yugoslavia, Romania and Spain, some right up to
the end of the war. Surviving SM.79s were converted into transports
during the last phases of the war, serving in that role until the early
1950s.
|
Specifications:
|
|
Savoia-Marchetti
S.M.79 Sparviero |
|
Dimensions:
|
|
Wing span:
|
69 ft 6 1/2 in
(21.2 m) |
|
Length:
|
53 ft 1 3/4 in
(16.2m) |
|
Height:
|
13 ft 5.5 in (4.1
m) |
|
Weights:
|
|
Empty: |
16,755 lb (7,600
kg) |
|
Operational:
|
24,192 lb (11,300
kg) |
|
Performance:
|
|
Maximum Speed:
|
270 mph (434 km/h)
|
|
Service Ceiling:
|
23,000 ft (7,000 m)
|
|
Range: |
1,243 miles (2,000
km) |
|
Powerplant:
|
|
Powered by three
559 kW (750 hp) Alfa-Romeo 126 RC.34 radials. Later three
Piaggio P.XI RC40 1,000 hp 14-cylinder radial. The twin-engined
S.M. 79B variety. Romania built the 79JR under license with two 894
kW (1,200 hp) Junkers Jumo 211Da liquid-cooled engines.
|
|
Armament:
|
|
It carried a 12.7 mm Breda-SAFAT gun firing ahead from the
roof of the cockpit humpback that enabled bullets to clear the nose
propeller; a second firing to the rear from the hump; a third aimed
down and to the rear from the gondola under the rear fuselage; and
often a 7.7 mm firing from each beam window. this needing a crew of
at least five. The bombardier occupied the gondola with his legs
projecting down in two retractable tubes during the bombing run. Up
to 1,000 kg (2,205 lb) of bombs were carried in an internal bay;
alternatively two 450 mm (17.7 in) torpedoes could be hung
externally.
|
|
