
measurement
Knots and Nautical
Miles
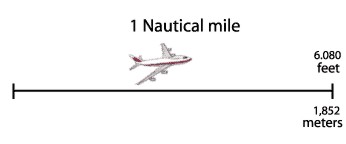
All navigation uses the Nautical Mile as the unit of distance.
Traditionally a nautical mile is 6,080 feet but more precisely 6,076.11549 feet.
In metric measurement it is 1,852 meters, which is one minute of arc of a great
circle of the Earth. Even under the metric system, the unit of distance for
navigation is still called the nautical mile. One knot converted to miles per
hour (mph) would be approximately 1.15 mph. One mile per hour would be 0.868
knots. A statute mile is the common "mile" with a length of 5,280 feet.
Therefore a statute mile is not as long as a nautical mile. One nautical mile
would equal approximately 1.15 statute miles. Making the conversion from
nautical miles to statute miles would be done as 120 nautical miles x 1.15
statute miles = 138 statute miles. Converting from statute to nautical miles
would require dividing by 1.15. Therefore 200 statute miles would equal (200 /
1.15 = 174) 174 nautical miles.
Many of the air navigational terms come from our heritage of sea
navigation. In the days of wooden sailing vessels, the speed of a sailing ship
was measured by unravelling a knotted rope into the water behind the moving ship.
The number of knots in the rope that passed over the railing in a given amount
of time would indicate how fast the ship was moving (its number of knots). It is
this same term that is used in aeronautics and aviation to indicate flight
speed, however without the knotted rope trailing behind the
aircraft.
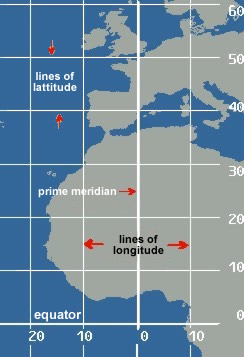
Latitude / Longitude
A reference system is used with which an exact location on the Earth's
surface can be pinpointed. This system uses designated lines of latitude and
longitude. Latitude measures north and south of the equator, and longitude
measures east and west of the prime meridian (located in Greenwich, England). The
latitude of an exact location is expressed in terms of degrees, minutes and
tenths of a minute. One minute of latitude equals 1/60th of a degree. The North
Pole, for example, is 90 degrees north of the equator. This is written as
N9000.0. The South Pole is located at 90 degrees south of the equator and is
written as S9000.0. The longitude of an exact location is expressed in terms of
degrees, minutes and tenths of a minute, also. One minute of longitude equals
1/60th of a degree. The longitude of the airport at Miami, Florida is located,
for example, approximately 80 degrees west of the prime meridian. Precisely,
this is written as W08016.6, and expressed as 80 degrees and 16.6 minutes west
of the zero meridian. The airport at Perth, Australia is located approximately
115 degrees east of the zero meridian and is written as E11557.5. This is
expressed as 115 degrees and 57.5 minutes east. Combining both latitude and
longitude, the location of the airport in Miami, Florida is N2547.1 and
W08016.6. This measure is used globally and communicates clearly to all pilots
the same locations.
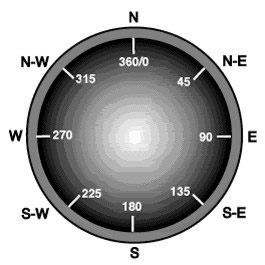
Compass Directions
In
navigation and surveying all measurement of direction is performed by using the
numbers of a compass. A compass is a 360° circle where 0/360° is North, 90° is
East, 180° is South, and 270° is West.
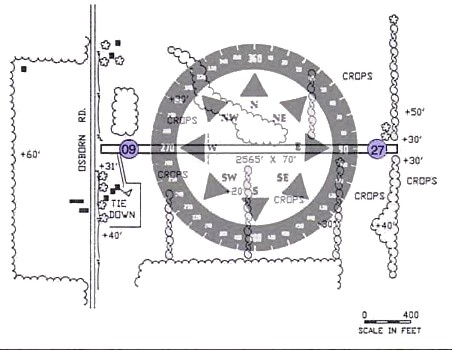
Each
runway has a different number on each end. Look at the diagram below. One end of
the runway is facing due west while the other end of the runway is facing due
east. The compass direction for due west is 270 degrees ("27"). The compass
direction for due east is 90 degrees ("9"). All runways follow this directional
layout. This runway would be referred to as "Runway 9-27" because of its
east-west orientation.
Applying this to navigation means that pilots do not turn right or
left, or fly east or south exactly. To fly east the pilot would take a heading
of 90° . To fly south, the compass heading would be 180°. Look at the compass
below to note the compass headings for northeast, southwest and west.
|
